
Coursework highlights
Simulation and Modeling of Advanced Manufacturing Processes
Semi-analytical modeling of manufacturing processes:
- Multiphysical modelling taking into account mechanics, material properties, heat, electricity, and magnetism
- Simplify complex equations by making qualified assumptions to make the math manageable
- Run time-stepping code to dynamically calculate and update all variables
This provides an in-depth intuition for the processes
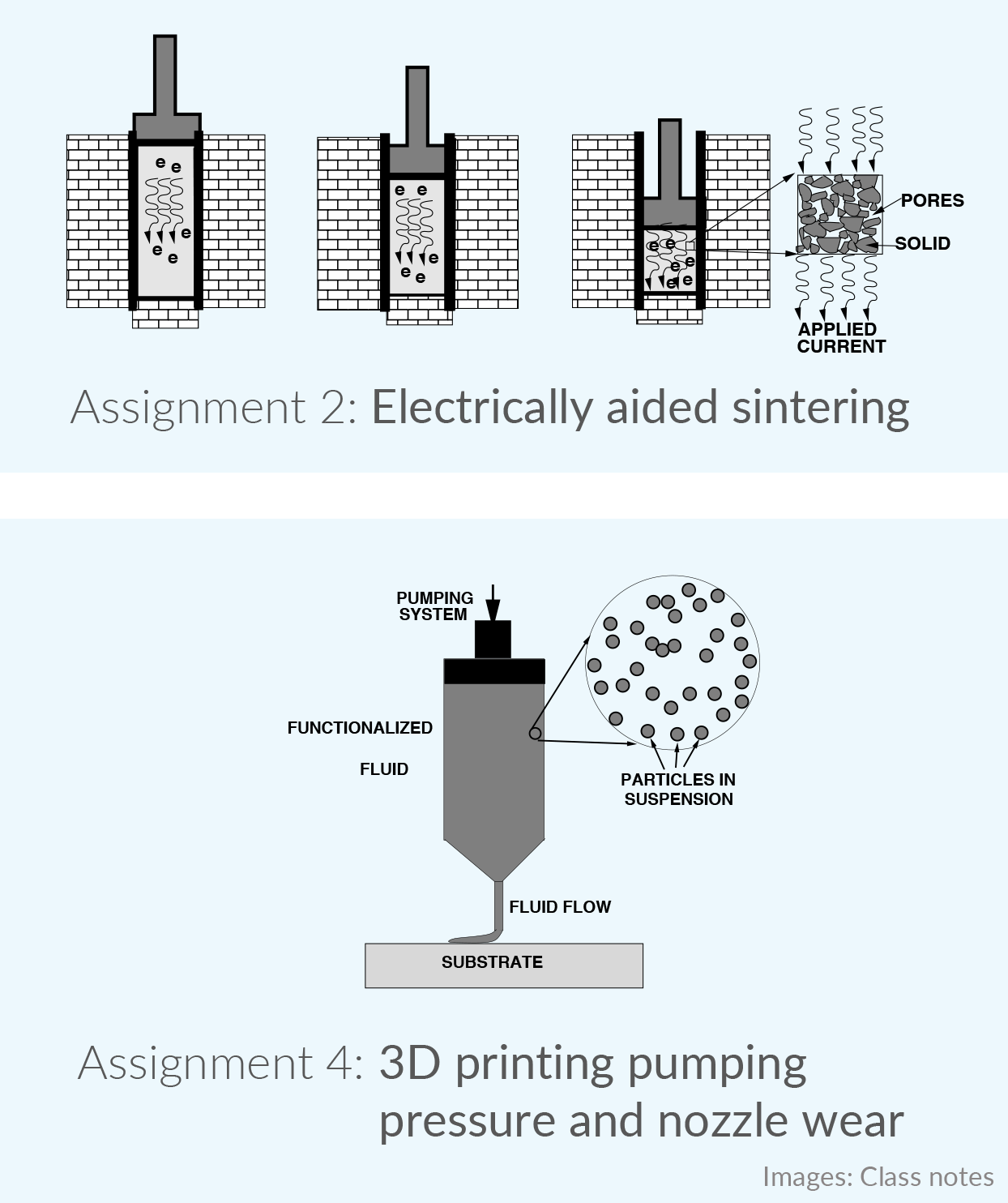
Theory of Electron Microscopy and X-ray Diffraction
Electron Microscopy Laboratory
Two courses dedicated to microscopy, including a lab course with over 50 hours of TEM time
- Characterization of engineering materials by electron microscopy, diffraction, and spectroscopy
- Characterization of defects
- In-depth coverage of the theory of operation of a TEM in all diffraction and imaging modes
- Included over 50 hours of TEM time over the semester, in small teams of three.
Images obtained by tilting the TEM stage.
These images were used to produce a 3D reconstruction (see below).
Video: Assignment, own work
Reconstructed 3D model.
Images across a larger range of angles will give a better reconstruction.
Video: Assignment, own work
Computational Materials Science
Introductory computational materials science course covering multiple computational techniques.
Spent one month each working on projects in
- Empirical energy methods
- Density Functional Theory (DFT)
- Monte Carlo Methods
- Molecular Dynamics
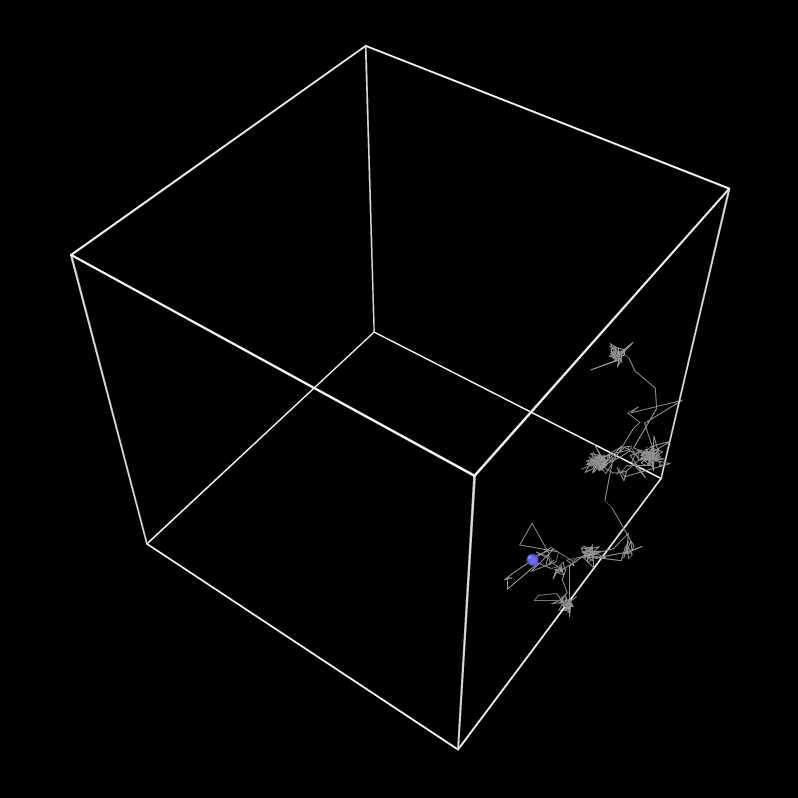
Diffusion of a Hydrogen atom in a matrix of Palladium, from a Molecular Dynamics simulation
System contains 500 Pd atoms and 10 H atoms in total. Temperature = 950 K. 50 ps run with a coordinate dump every 0.1ps.
Image: Assignment, own work
Mechanics of Solids
Elements of Solid Mechanics
UE 204
Two courses covering analytical and numerical treatment of mechanics of solids
- Axial, shear, and torsion of simple bodies
- Theory of simple bending, and stress distribution in beams
- Principal stresses and strains, Mohr’s diagram
- Energy methods, Principal of virtual work, and Castigliano’s theorem
- Continuum mechanics: stress and strain tensors, equilibrium, compatibility
- Three-dimensional elastic, plastic, and viscoelastic problems
- Thermal, transformation, and dealloying stresses
- Stress concentrations, plane problems, metal forming problems
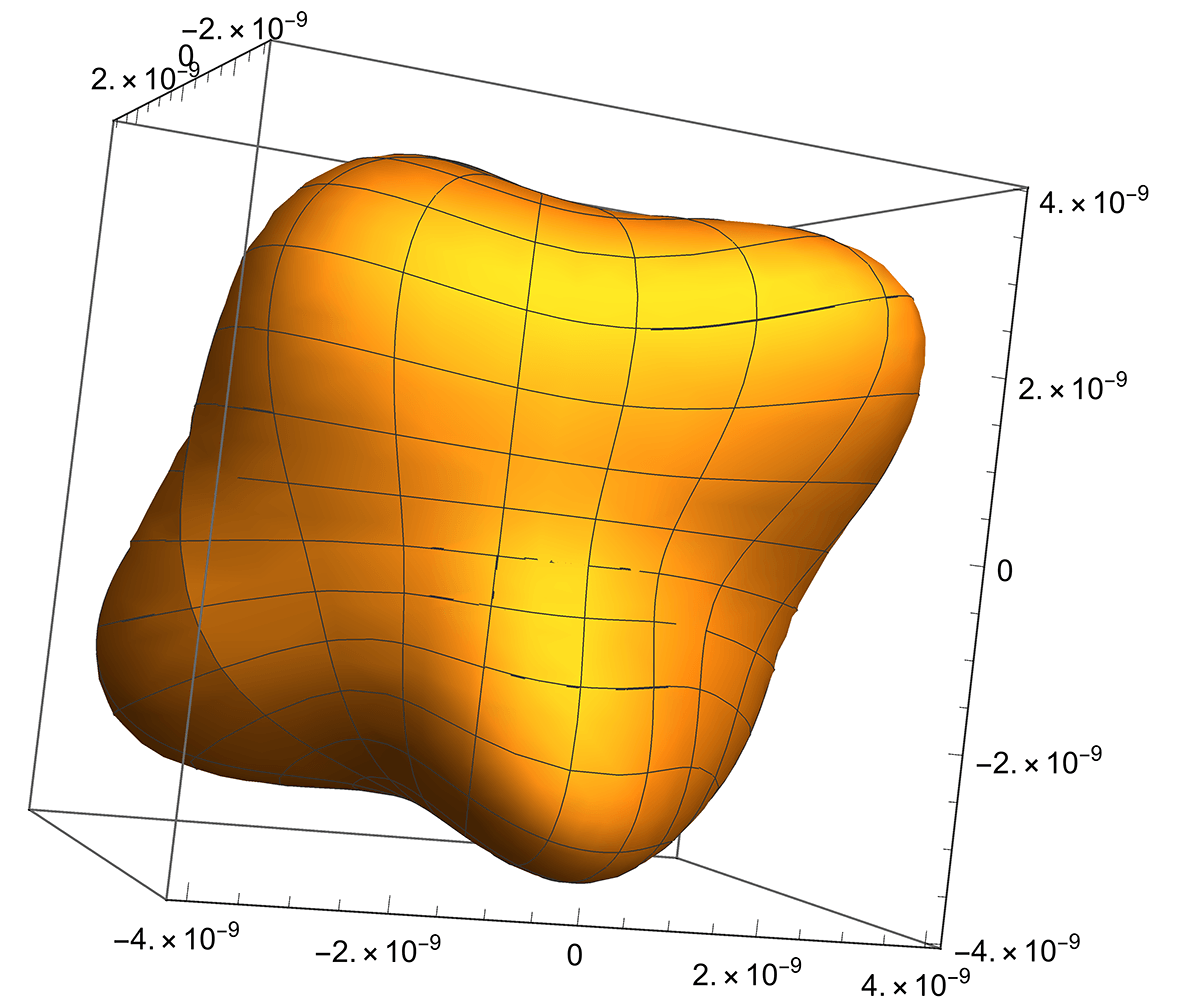
Anisotropic materials exhibit non-uniform properties in different directions.
This image shows Young’s modulus of Copper Sulphate as a function of sample orientation. Different orientations (with respect to the crystallographic axes) show different Young’s moduli
Image: Assignment, own work
Microstructural Design and Development of Engineering Materials
How can engineering materials be tailored to achieve the required properties?
- Importance of composition, process, and microstructure in the resultant properties of materials
- Covered: Aluminum alloys, Steels, Titanium alloys, Ni-base superalloys, and Magnesium alloys
- Discussed modifications due to alloying additions, heat treatment, ageing, tempering, phase control through processing conditions, etc.
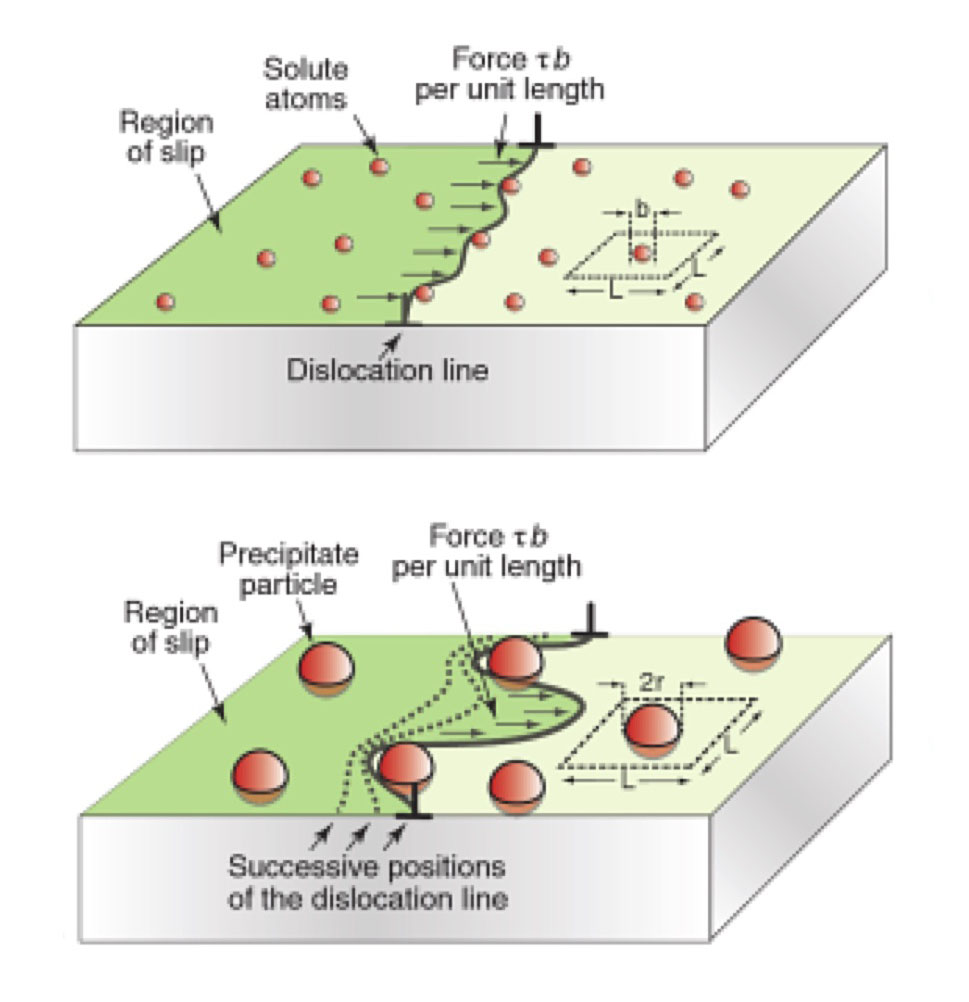
Strengthening due to solute atoms and precipitates.
Image: Class notes
Polymer Science and Engineering
Polymer blends and Nanocomposites
Polymer manufacturing and processing
Behaviour with blending and composite additions
- Chemistry and process aspects of manufacturing.
- Polymer processing including thermoforming, extrusion and injection moulding, and blow moulding.
- Behaviour of blends and composites with respect to viscosity, processability, mechanical properties, conductivity, etc.
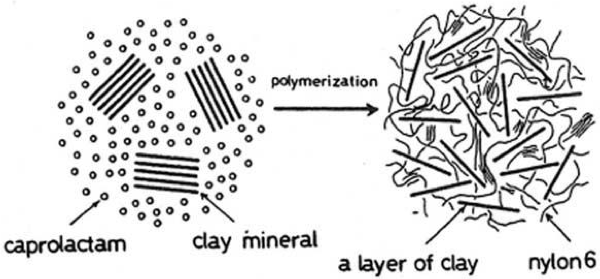
Nylon-6/clay nanocomposite
Used in the automotive industry since the late 1990s.
Image: Class notes
Materials Thermodynamics, Materials Kinetics,
Microstructures in Materials, Phase transformations
4 courses dedicated to core physical metallurgy
Covers:
- Diffusion
- Phase diagrams
- Microstructure evolution
- Sintering
- Nucleation and grain growth
and many other related topics
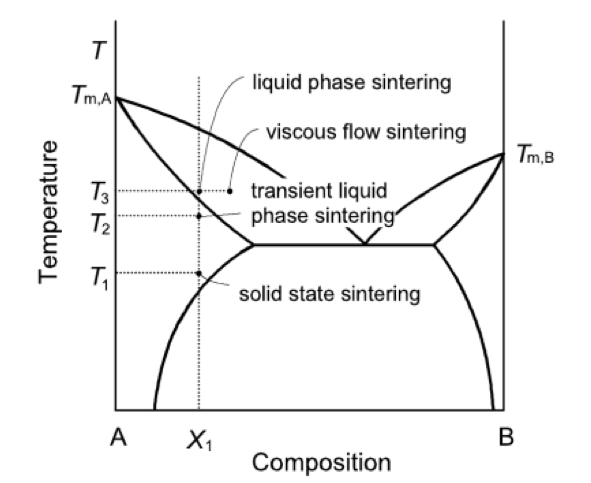
Sintering in different phase regions.
Image: Class notes
Solidification processing
Theoretical physics-based approach to solidification
- Segregation
- Gibbs-Thomson effect (dependence of segregation on size)
- Transport processes in solidification
- Instabilities, dendritic growth
- Eutectic and peritectic growth
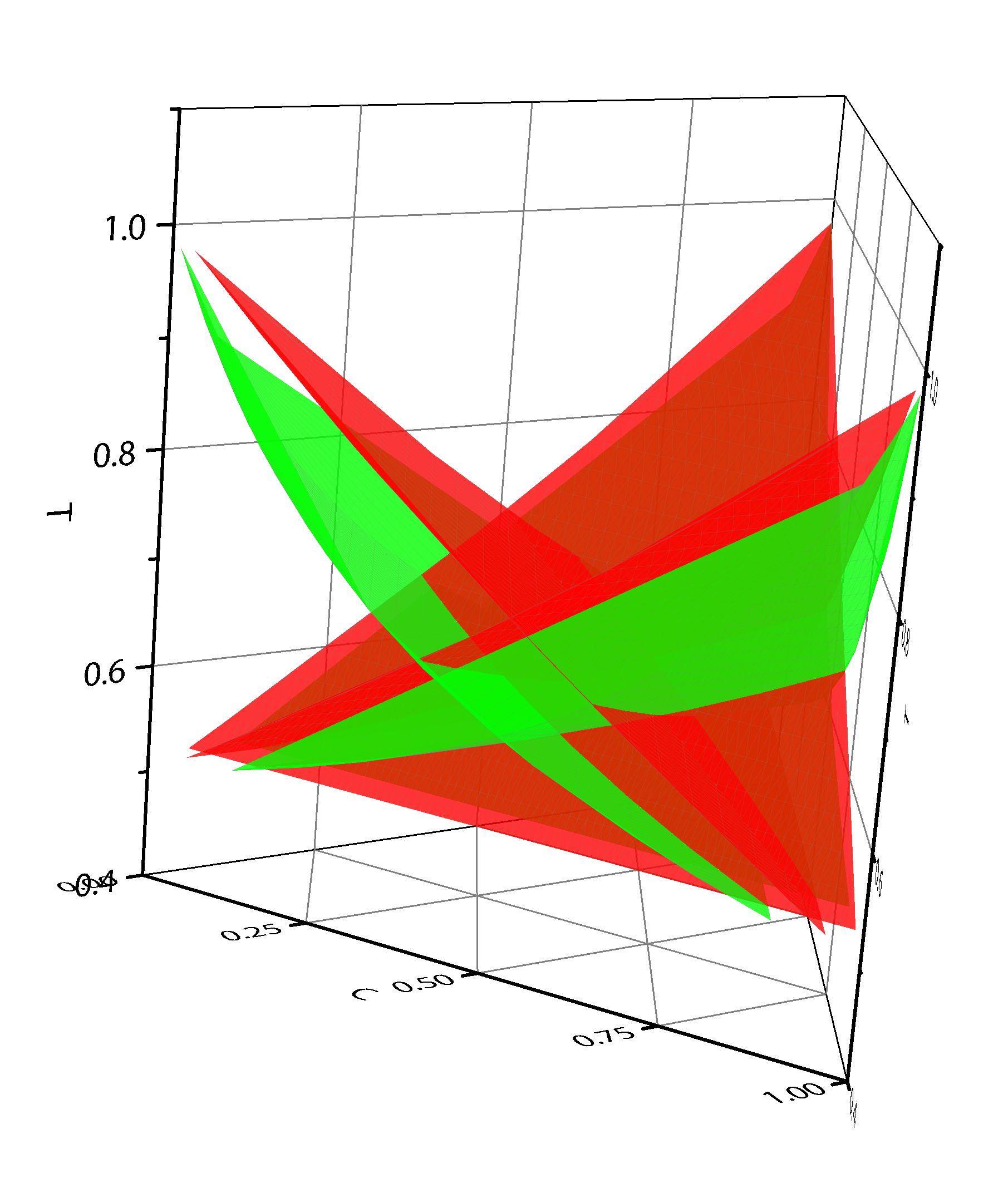
Ternary isomorphous phase diagram, calculated from differential equations using Gibbs free energies
Image: Assignment, own work
Science of Materials Processing
Main topics
- Deformation processes
- Powder metallurgy
- Process maps
Mechanisms covered:
- Plasticity, yield, flow instability, drawability, anisotropy
- Sensitivity to temperature and strain rate
- Thermally activated deformation
- Powder processing
Also covered: Casting and joining, welding, recovery and recrystallization, softening mechanisms
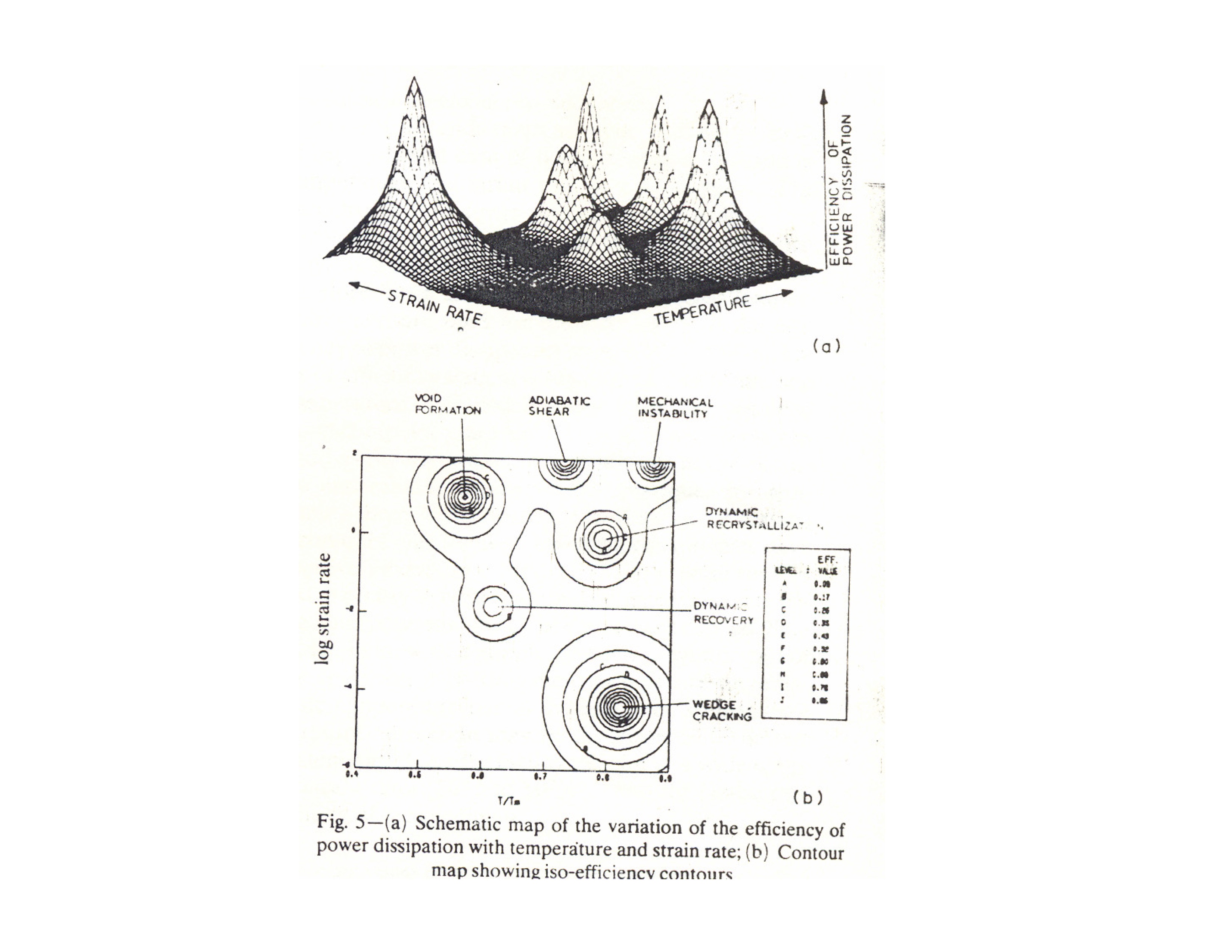
Process maps
Image: Class notes